Building Reusable Components with Ruby Rack: A Practical Guide to Middleware in Rails 17/03/2023 ~ Views: 1356
Ruby Rack: A Brief Introduction
Ruby Rack is a web server interface for Ruby that allows web applications to be built as middleware. Rack provides a modular and flexible framework for developing web applications that can be easily integrated with various web servers, including Apache and Nginx.
Why Use Ruby Rack?
Rack provides a standard interface for web servers, allowing developers to focus on building web applications instead of worrying about server-specific details. This makes it easier to deploy web applications across multiple servers and platforms. Additionally, Rack middleware allows for the creation of reusable components that can be shared across different applications.
Practical Examples of Using Ruby Rack in a Rails App
Let's take a look at some practical examples of using Ruby Rack in a Rails app.
- Implementing Middleware
Middleware is software that runs between the server and the application, allowing developers to add additional functionality to the application. Rack middleware can be used to perform tasks such as authentication, logging, and caching.
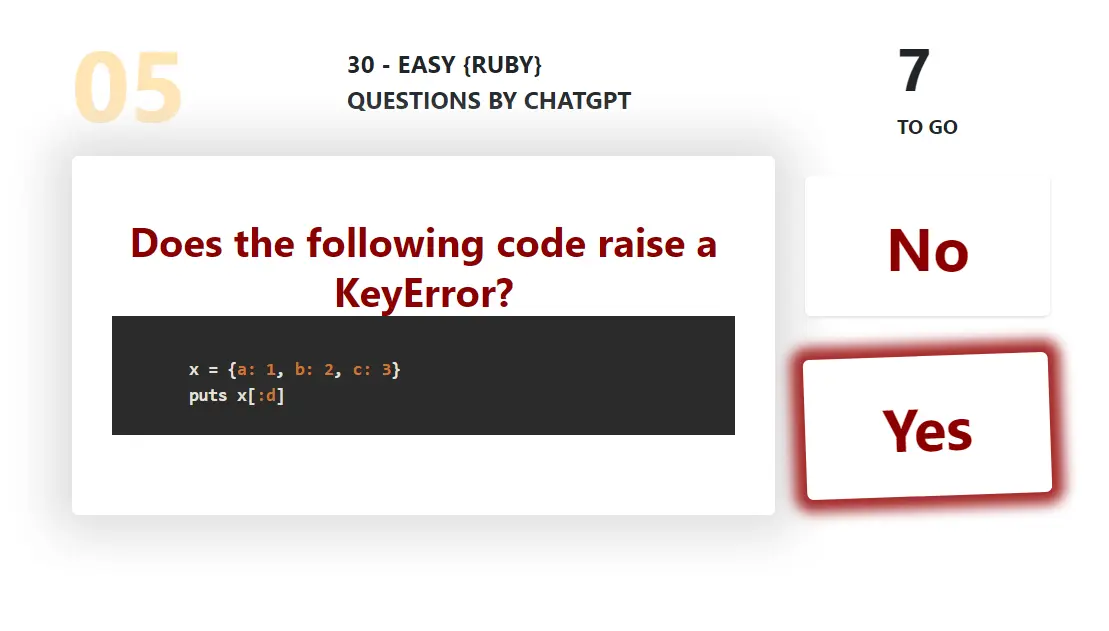
To implement middleware in a Rails app, create a new class in the app/middleware directory. The class should implement the call method, which takes the env parameter representing the current request environment. The call method should return an HTTP response.
Here's an example of middleware that logs the request URL:
# app/middleware/logger.rb
class Logger
def initialize(app)
@app = app
end
def call(env)
puts "Request URL: #{env['REQUEST_URI']}"
@app.call(env)
end
end
# config/application.rb
config.middleware.use LoggerIn the above code, we define a Logger class that takes the app parameter in the constructor. The call method logs the request URL and then passes the request on to the next middleware in the chain using @app.call(env). Finally, we add the middleware to the middleware stack in config/application.rb.
- Custom Routing
Rack can also be used to implement custom routing in a Rails app. To do this, create a new class in the app/middleware directory that implements the call method.
Here's an example of a custom router that maps requests to different controllers based on the URL:
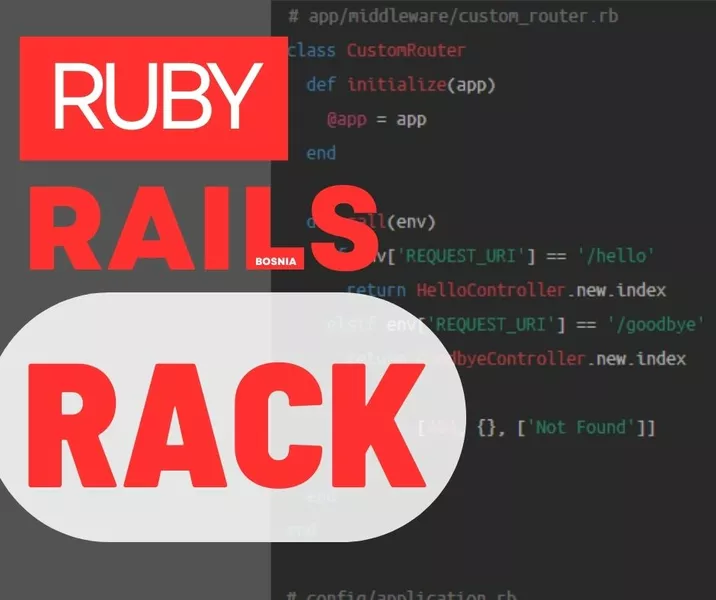
# app/middleware/custom_router.rb
class CustomRouter
def initialize(app)
@app = app
end
def call(env)
if env['REQUEST_URI'] == '/hello'
return HelloController.new.index
elsif env['REQUEST_URI'] == '/goodbye'
return GoodbyeController.new.index
else
return [404, {}, ['Not Found']]
end
end
end
# config/application.rb
config.middleware.use CustomRouterIn the above code, we define a CustomRouter class that takes the app parameter in the constructor. The call method maps requests to different controllers based on the URL. Finally, we add the middleware to the middleware stack in config/application.rb.
Conclusion
Ruby Rack is a powerful tool for building web applications in Ruby. It provides a flexible and modular framework that makes it easy to develop and deploy web applications across multiple servers and platforms. With the examples above, you should now have a better understanding of how to use Rack in your Rails app.
Tags: #rubyrack #middleware #customrouting #rails #webdevelopment #webservers #reusablecomponents #chatgpt